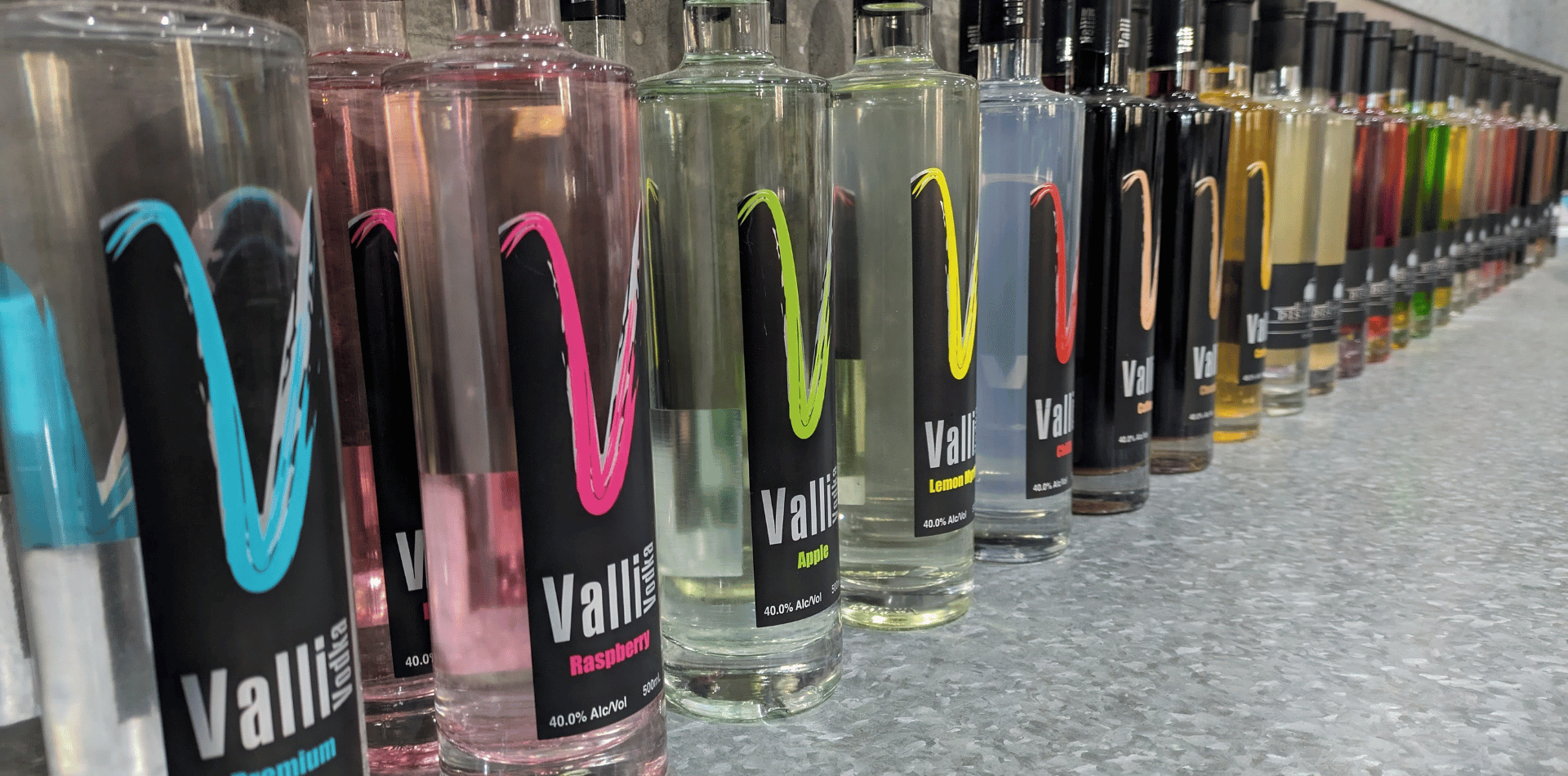HUNTER DISTILLERY
Pokolbin's Original Distillery
At Hunter Distillery compromise is not an option.
Source only the best ingredients available.
Use traditional time proven methods.
Balanced with the latest production and quality control.
Add a whole lot of passion and some hard work.
Keeping the craft alive.
All our products are
Hand-crafted on-site
FROM NATURAL RAW INGREDIENTS.
AWARD WINNING
GIN AND VODKA DISTILLERY
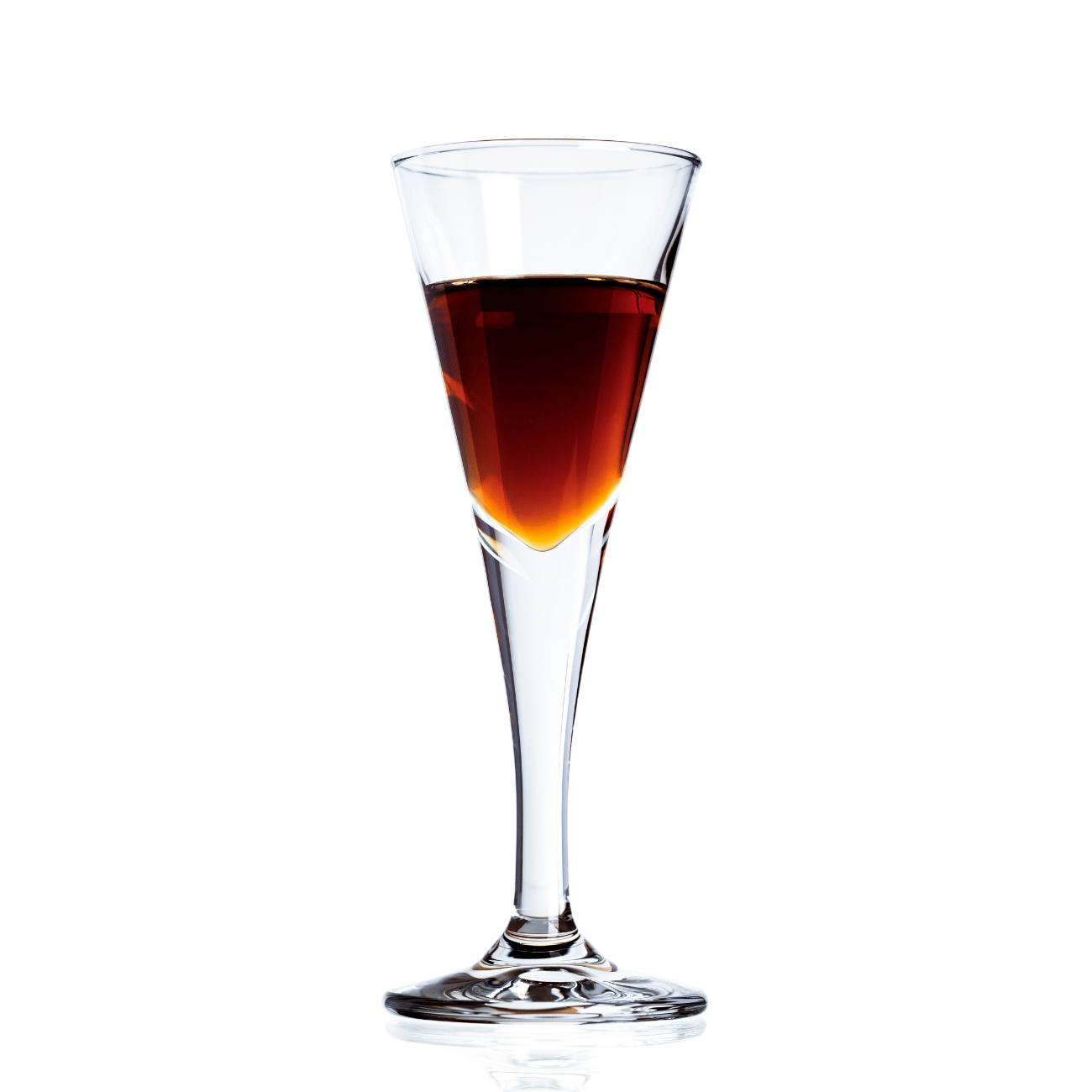
SILK
Inspired by our youngest daughter, Anna, and influenced by 4 generations of distillers, Silk is a sophisticated, delectable almond vodka liqueur.
Unique in the spirits world, the silk range is vegan friendly, gluten free, and only made with natural ingredients. We don't compromise quality at Hunter Distillery, which is why we maintain our tradition of making 100% of our products in-house from scratch.
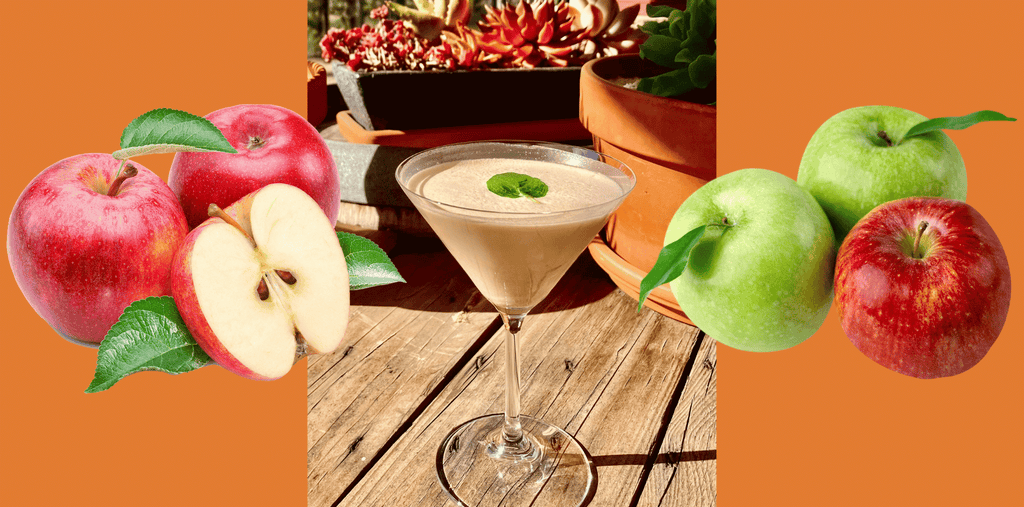
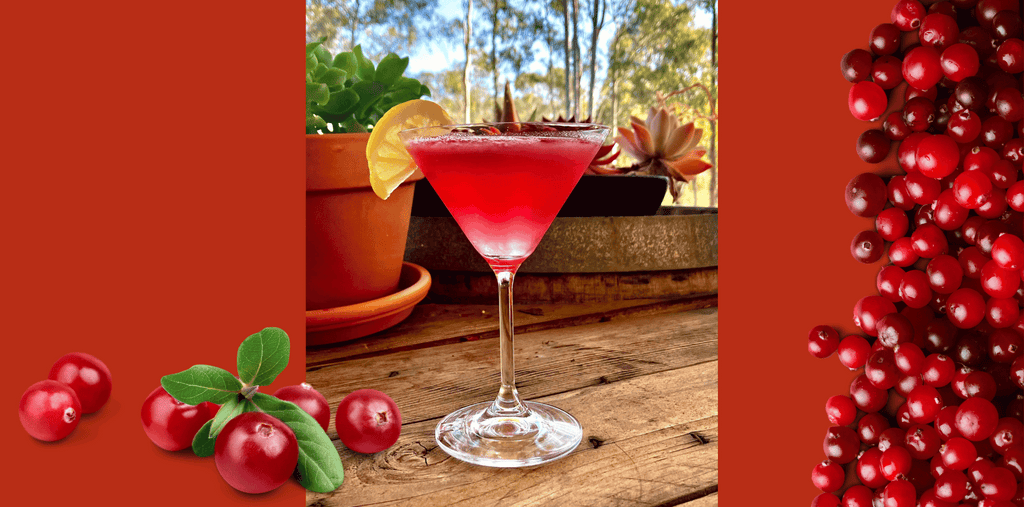
Silk can be appreciated neat, on ice, warmed by a fire, or added to a creamy cocktail or desert.
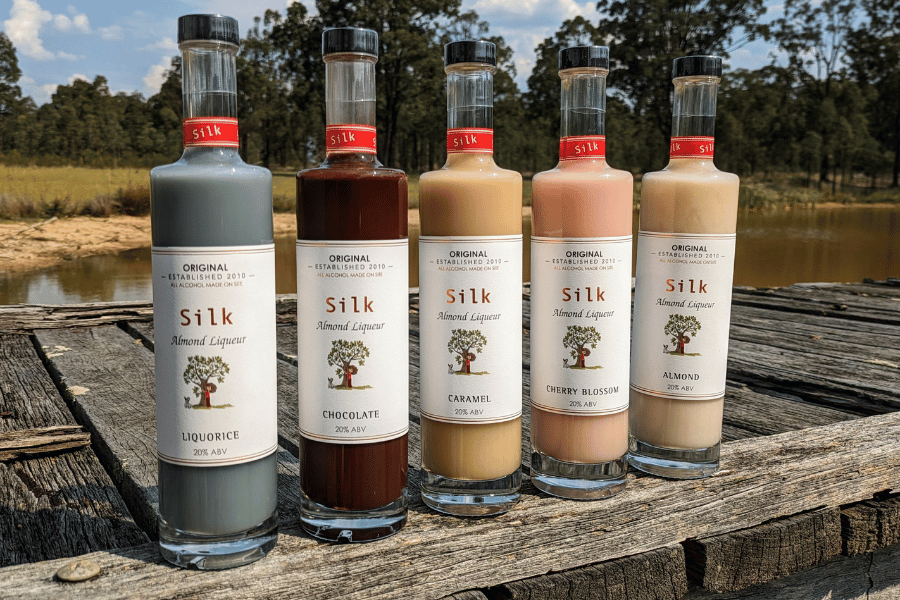

Our Best Sellers
Vodka is not just a drink,
it's a state of mind.
Some of Our Popular Recipes
Are You Ready?
Be the first to hear about limited releases, special events and exclusive distillery news.
The History of Gin Distilling
The history of gin distilling is a fascinating journey that spans several centuries, marked by cultural, social, and scientific developments.
Origins of Gin
Gin's roots can be traced back to the early distilled spirits of the Middle Ages. The precursor to gin was a medicinal liquor known as "jenever" (or genever), which was first produced in the Netherlands in the 13th century.
Jenever was made by distilling malt wine and then flavouring it with juniper berries, which were believed to have medicinal properties.
The Birth of Gin
The transition from jenever to gin as we know it began in the 16th century. English soldiers fighting in the Low Countries during the Eighty Years' War brought back jenever, which they called "Dutch Courage," to England. Over time, the English adapted the recipe, leading to the creation of gin. By the 17th century, gin was being produced in England, where it gained popularity, especially during the reign of William of Orange, who actively promoted gin production.
The Gin Craze
The 18th century saw what is now known as the "Gin Craze" in England. Gin became incredibly popular, especially among the urban poor, due to its low cost and widespread availability. This period was characterised by excessive consumption and social problems, leading to a series of governmental crackdowns, including the Gin Acts of the 18th century. These Acts aimed to reduce gin consumption by raising taxes on its production and sale, which gradually curbed the craze.
Refinement and Regulation
In the 19th century, gin distillation techniques improved significantly with the invention of the column still (or continuous still), which allowed for the production of a cleaner, higher-quality spirit. This period also saw the rise of "London Dry Gin," a style of gin that is still popular today. London Dry Gin is known for its crisp, juniper-forward flavour and lack of added sweeteners or flavourings after distillation.
The Modern Era
The 20th century brought about a decline in gin's popularity, particularly during Prohibition in the United States, when gin was often illicitly produced as "bathtub gin." However, gin saw a resurgence in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, driven by the craft distilling movement. Today, gin is celebrated for its versatility and the wide range of botanicals that can be used to flavour it, leading to the creation of many new and innovative gin styles.
Global Expansion
Gin distilling has spread across the globe, with distilleries in countries far beyond its European origins. Modern gin production incorporates a diverse array of botanicals and regional influences, reflecting the spirit’s global appeal. From the classic London Dry to contemporary gins infused with exotic ingredients, gin continues to evolve while maintaining its historical roots.
Gin's history is one of evolution—from a medicinal liquor to a beloved spirit, shaped by cultural trends, technological advancements, and global influences.